연결 리스트 (Linked List)
연결 리스트(Linked List)는 노드(Node)들의 연결을 통해 데이터를 저장하는 동적 자료구조이다.
각 노드는 데이터(Data)와 다음 노드를 가리키는 포인터(Next)로 구성되며, 필요에 따라 동적으로 크기를 조절할 수 있다.
배열과 달리 메모리의 연속적인 공간을 요구하지 않으며, 삽입/삭제 연산이 효율적이다.
연결 리스트는 유연한 메모리 관리와 효율적인 삽입/삭제 연산으로 인해 다양한 응용 분야에서 활용되는 중요한 데이터 구조이다. 배열에 비해 특정 위치 접근이 느리지만, 동적 크기 조정과 삽입/삭제 연산의 효율성은 큰 장점이다.
다양한 형태(단일, 이중, 원형)와 최적화 기법(센티넬 노드, 런너 기법 등)을 적절히, 활용하면 복잡한 문제도 효율적으로 해결할 수 있다. 특히 스택, 큐, 해시 테이블, 그래프 등 다른 자료구조의 구현에도 널리 사용되어 알고리즘과 데이터 구조를 이해하는 데 필수적인 개념이다.
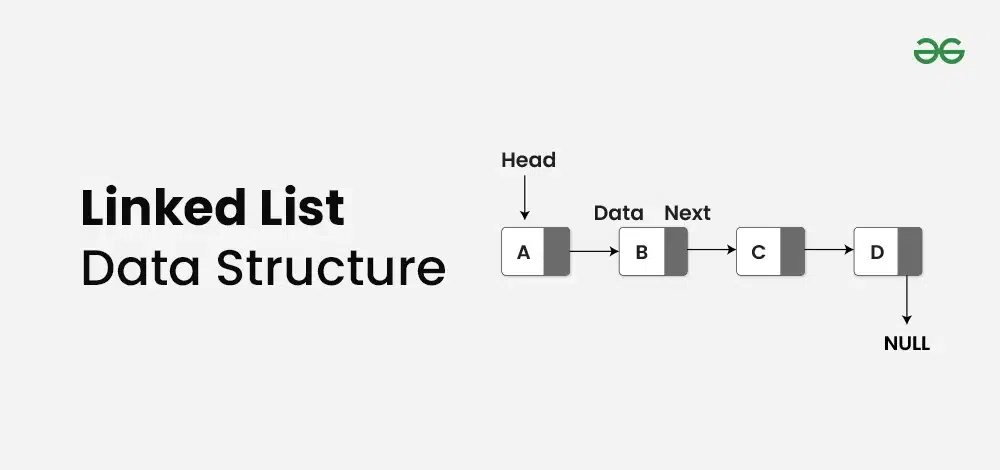
연결 리스트의 기본 개념
연결 리스트는 여러 노드들이 연결된 형태로 구성된다.
각 노드는 두 부분으로 나뉜다:
- 데이터 필드: 저장하고자 하는 실제 값
- 링크 필드: 다음 노드의 주소를 가리키는 포인터
가장 첫 번째 노드를 ‘헤드(Head)‘라고 부르며, 마지막 노드의 링크 필드는 보통 NULL을 가리켜 리스트의 끝을 표시한다.
연결 리스트의 장점
- 동적 메모리 할당을 통해 자료의 크기가 실행 시간에 맞춰 유연하게 조절된다.
- 삽입 및 삭제 시 배열과 달리 전체 데이터를 재배열하지 않아도 되므로 연산 효율이 높다.
- 메모리의 연속적인 할당이 필요 없기 때문에, 메모리 단편화 문제를 줄일 수 있다.
연결 리스트의 단점
- 각 노드에 추가적인 포인터가 필요하므로, 메모리 오버헤드가 발생한다.
- 데이터가 메모리상에 흩어져 있어 캐시 인접성(cache locality)이 떨어지고, 이로 인해 캐시 히트율이 낮아 성능 저하가 나타날 수 있다.
- 임의의 데이터 접근을 위해 전체 노드를 순회해야 하므로 검색 속도가 느리다.
연결 리스트의 종류
단일 연결 리스트(Singly Linked List)
각 노드가 다음 노드만을 가리키는 가장 기본적인 형태이다.
한 방향으로만 탐색이 가능하다.
이중 연결 리스트(Doubly Linked List)
각 노드가 이전 노드와 다음 노드를 모두 가리키는 형태로, 양방향 탐색이 가능하다.
원형 연결 리스트(Circular Linked List)
마지막 노드가 첫 번째 노드를 가리키는 형태로, 리스트의 끝이 없다.
단일 또는 이중 연결 리스트 모두 원형으로 구현할 수 있다.
| |
연결 리스트의 주요 연산과 시간 복잡도
| 연산 | 설명 | 시간 복잡도 |
|---|---|---|
| 접근 (Access) | 특정 노드에 접근하려면 순차 탐색이 필요 (O(n)) | O(n) |
| 탐색 (Search) | 특정 값을 찾기 위해 노드를 순회해야 함 (O(n)) | O(n) |
| 삽입 (Insert) | 처음 또는 중간에 삽입 시 포인터 조정만 필요 (O(1)) | O(1) |
| 삭제 (Delete) | 특정 노드를 삭제 시 포인터 조정만 필요 (O(1)) | O(1) |
접근(Access)
- 특정 인덱스의 요소에 접근: O(n)
- 연결 리스트는 인덱스를 통한 직접 접근이 불가능하여, 원하는 위치까지 순차적으로 탐색해야 한다.
검색(Search)
- 특정 값을 가진 노드 검색: O(n)
- 헤드부터 시작하여 원하는 값을 찾을 때까지 순차적으로 탐색한다.
삽입(Insertion)
- 리스트 시작 부분에 삽입(헤드 삽입): O(1)
- 리스트 끝 부분에 삽입(단일 연결 리스트): O(n) - 끝을 찾기 위해 전체 탐색 필요
- 리스트 끝 부분에 삽입(이중 연결 리스트, 테일 포인터 사용): O(1)
- 특정 위치에 삽입: O(n) - 위치 찾기 위한 탐색 필요
삭제(Deletion)
- 리스트 시작 부분 삭제(헤드 삭제): O(1)
- 리스트 끝 부분 삭제(단일 연결 리스트): O(n)
- 리스트 끝 부분 삭제(이중 연결 리스트, 테일 포인터 사용): O(1)
- 특정 위치/값 삭제: O(n)
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 14 15 16 17 18 19# 단일 연결 리스트에서 특정 값을 가진 노드 삭제 def delete_node(self, key): # 빈 리스트 체크 if self.head is None: return # 헤드 노드가 삭제할 값을 가지는 경우 if self.head.data == key: self.head = self.head.next return # 삭제할 노드 탐색 current = self.head while current.next and current.next.data != key: current = current.next # 값을 찾은 경우 if current.next: current.next = current.next.next
연결 리스트의 메모리 구조
연결 리스트의 각 노드는 메모리 상에 불연속적으로 위치할 수 있다.
각 노드는 데이터와 포인터를 위한 공간을 필요로 하며, 이 포인터가 다음 노드의 메모리 주소를 가리킨다.
예를 들어, 4바이트 정수를 저장하는 단일 연결 리스트에서 각 노드는:
- 4바이트: 데이터(정수)
- 4
8바이트: 다음 노드 포인터12바이트의 메모리를 사용하는 반면 배열은 요소당 4바이트만 필요로 한다.
총 8
연결 리스트의 응용
스택 및 큐 구현
연결 리스트는 스택과 큐를 효율적으로 구현하는 데 사용될 수 있다.1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 14 15 16 17# 연결 리스트를 사용한 스택 구현 class Stack: def __init__(self): self.top = None def push(self, data): new_node = Node(data) new_node.next = self.top self.top = new_node def pop(self): if self.top is None: return None data = self.top.data self.top = self.top.next return data해시 테이블 충돌 해결
해시 테이블에서 충돌이 발생했을 때, 연결 리스트를 사용하여 체이닝(chaining) 방식으로 충돌을 해결할 수 있다.1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 14 15 16 17 18 19 20 21 22 23 24 25 26 27 28 29 30 31 32 33 34 35 36 37 38 39 40 41 42 43 44 45 46 47 48 49class Node: def __init__(self, key, value): self.key = key self.value = value self.next = None class HashTable: def __init__(self, size): self.size = size self.table = [None] * size # 해시 테이블 배열 def hash_function(self, key): return hash(key) % self.size def insert(self, key, value): index = self.hash_function(key) new_node = Node(key, value) if self.table[index] is None: # 해당 버킷이 비어있으면 직접 삽입 self.table[index] = new_node else: current = self.table[index] # 충돌 발생 -> 연결 리스트 사용 while current.next: if current.key == key: current.value = value # 기존 키 업데이트 return current = current.next current.next = new_node # 마지막 노드에 추가 def search(self, key): index = self.hash_function(key) current = self.table[index] while current: if current.key == key: return current.value current = current.next return None # 찾지 못하면 None 반환 # 해시 테이블 사용 예시 hash_table = HashTable(5) hash_table.insert("apple", 100) hash_table.insert("banana", 200) hash_table.insert("cherry", 300) hash_table.insert("apple", 150) # 업데이트 print(hash_table.search("apple")) # 150 print(hash_table.search("banana")) # 200 print(hash_table.search("grape")) # None (없음)그래프 표현
인접 리스트(adjacency list)를 통해 그래프를 표현할 때 연결 리스트가 사용된다.1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 14 15 16 17 18 19 20 21 22 23 24 25class Graph: def __init__(self, vertices): self.V = vertices self.adj_list = {i: [] for i in range(vertices)} # 각 노드마다 연결 리스트 생성 def add_edge(self, u, v): self.adj_list[u].append(v) # u -> v 방향 간선 추가 self.adj_list[v].append(u) # 무방향 그래프일 경우 v -> u도 추가 def display(self): for vertex, neighbors in self.adj_list.items(): print(f"{vertex} -> {neighbors}") # 그래프 생성 및 간선 추가 graph = Graph(5) graph.add_edge(0, 1) graph.add_edge(0, 4) graph.add_edge(1, 2) graph.add_edge(1, 3) graph.add_edge(1, 4) graph.add_edge(2, 3) graph.add_edge(3, 4) # 그래프 출력 graph.display()다항식 표현
다항식의 각 항을 노드로 표현하여 다항식 연산을 효율적으로 수행할 수 있다.1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 14 15 16 17 18 19 20 21 22 23 24 25 26 27 28 29 30 31 32 33 34 35 36 37 38 39 40 41 42 43 44class Term: def __init__(self, coefficient, exponent): self.coefficient = coefficient # 계수 self.exponent = exponent # 차수 self.next = None # 다음 항을 가리키는 포인터 class Polynomial: def __init__(self): self.head = None # 첫 번째 항 def add_term(self, coefficient, exponent): new_term = Term(coefficient, exponent) if not self.head or self.head.exponent < exponent: new_term.next = self.head self.head = new_term return current = self.head while current.next and current.next.exponent > exponent: current = current.next if current.next and current.next.exponent == exponent: current.next.coefficient += coefficient # 같은 차수 항이면 계수 더하기 else: new_term.next = current.next current.next = new_term def display(self): current = self.head result = [] while current: result.append(f"{current.coefficient}x^{current.exponent}") current = current.next print(" + ".join(result)) # 다항식 표현 예시 poly1 = Polynomial() poly1.add_term(3, 2) # 3x^2 poly1.add_term(5, 3) # 5x^3 poly1.add_term(2, 1) # 2x^1 poly1.add_term(4, 3) # 기존 5x^3에 4 추가 -> 9x^3 poly1.display() # 출력: 9x^3 + 3x^2 + 2x^1
실제 연결 리스트 구현 예제
단일 연결 리스트 전체 구현
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 14 15 16 17 18 19 20 21 22 23 24 25 26 27 28 29 30 31 32 33 34 35 36 37 38 39 40 41 42 43 44 45 46 47 48 49 50 51 52 53 54 55 56 57 58 59 60 61 62 63 64 65 66 67 68 69 70 71 72 73 74 75 76 77 78 79 80 81 82 83 84 85 86 87 88 89 90 91 92 93 94 95 96 97 98 99 100 101 102 103 104 105 106 107 108 109 110 111 112class Node: def __init__(self, data): self.data = data self.next = None class SinglyLinkedList: def __init__(self): self.head = None # 리스트 끝에 노드 추가 def append(self, data): new_node = Node(data) # 리스트가 비어있는 경우 if self.head is None: self.head = new_node return # 마지막 노드 찾기 last = self.head while last.next: last = last.next # 마지막 노드의 다음을 새 노드로 설정 last.next = new_node # 리스트 시작에 노드 추가 def prepend(self, data): new_node = Node(data) new_node.next = self.head self.head = new_node # 특정 값 뒤에 노드 삽입 def insert_after(self, prev_value, data): # 리스트가 비어있는 경우 if self.head is None: return # 값 찾기 current = self.head while current and current.data != prev_value: current = current.next # 값을 찾지 못한 경우 if current is None: return # 새 노드 삽입 new_node = Node(data) new_node.next = current.next current.next = new_node # 특정 값을 가진 노드 삭제 def delete(self, value): # 빈 리스트 체크 if self.head is None: return # 헤드 노드가 삭제할 값을 가지는 경우 if self.head.data == value: self.head = self.head.next return # 삭제할 노드 탐색 current = self.head while current.next and current.next.data != value: current = current.next # 값을 찾은 경우 if current.next: current.next = current.next.next # 리스트 출력 def print_list(self): current = self.head while current: print(current.data, end=" -> ") current = current.next print("None") # 리스트 길이 계산 def length(self): count = 0 current = self.head while current: count += 1 current = current.next return count # 리스트 검색 def search(self, value): current = self.head position = 0 while current: if current.data == value: return position current = current.next position += 1 return -1 # 값을 찾지 못함 # 리스트 뒤집기 def reverse(self): prev = None current = self.head while current: next_node = current.next # 다음 노드 저장 current.next = prev # 현재 노드의 다음을 이전 노드로 변경 prev = current # 이전 노드를 현재 노드로 업데이트 current = next_node # 현재 노드를 다음 노드로 업데이트 self.head = prev # 헤드를 마지막 노드로 업데이트이중 연결 리스트 기본 구현
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 14 15 16 17 18 19 20 21 22 23 24 25 26 27 28 29 30 31 32 33 34 35 36 37 38 39 40 41 42 43 44 45 46 47 48 49 50 51 52 53 54 55 56class Node: def __init__(self, data): self.data = data self.prev = None self.next = None class DoublyLinkedList: def __init__(self): self.head = None self.tail = None # 리스트 끝에 노드 추가 def append(self, data): new_node = Node(data) # 리스트가 비어있는 경우 if self.head is None: self.head = new_node self.tail = new_node return # 끝에 새 노드 추가 self.tail.next = new_node new_node.prev = self.tail self.tail = new_node # 리스트 시작에 노드 추가 def prepend(self, data): new_node = Node(data) # 리스트가 비어있는 경우 if self.head is None: self.head = new_node self.tail = new_node return # 시작에 새 노드 추가 new_node.next = self.head self.head.prev = new_node self.head = new_node # 리스트 출력 (앞에서 뒤로) def print_forward(self): current = self.head while current: print(current.data, end=" <-> ") current = current.next print("None") # 리스트 출력 (뒤에서 앞으로) def print_backward(self): current = self.tail while current: print(current.data, end=" <-> ") current = current.prev print("None")
고급 연결 리스트 기법과 최적화
센티넬 노드(Sentinel Node)
더미 노드를 사용하여 예외 케이스 처리를 단순화한다.
특히 빈 리스트를 처리할 때 유용하다.1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 14 15class SinglyLinkedListWithSentinel: def __init__(self): self.sentinel = Node(None) # 센티넬 노드 self.size = 0 def append(self, data): new_node = Node(data) current = self.sentinel # 마지막 노드 찾기 while current.next: current = current.next current.next = new_node self.size += 1런너 기법(Runner Technique)
두 개의 포인터(빠른 포인터와 느린 포인터)를 사용하여 리스트를 탐색하는 기법이다.
중간 노드 찾기, 사이클 감지 등에 유용합니다.사이클 감지(Floyd’s Cycle-Finding Algorithm)
런너 기법을 응용하여 연결 리스트의 사이클(순환)을 감지하는 알고리즘이다.XOR 연결 리스트
메모리를 절약하기 위해 이중 연결 리스트에서 prev와 next 포인터 대신 XOR 연산을 사용하는 기법이다.
포인터 두 개 대신 하나로 양방향 탐색이 가능하다.
프로그래밍 언어별 연결 리스트 지원
C++
STL에서 std::list와 std::forward_list를 제공합니다.
std::list: 이중 연결 리스트std::forward_list: 단일 연결 리스트
Java
java.util 패키지에서 LinkedList 클래스를 제공한다. 이중 연결 리스트로 구현되어 있다.
JavaScript
내장 지원은 없지만 직접 구현이 가능합니다.
| |
Python
내장 지원은 없지만 collections 모듈의 deque가 이중 연결 리스트로 구현되어 있다.
연결 리스트 문제 해결 전략과 연습 문제
문제 해결 전략
- 경계 조건 확인: 빈 리스트, 단일 노드 리스트, 다중 노드 리스트 등
- 포인터 활용: 런너 기법, 여러 포인터 활용
- 재귀적 접근: 일부 문제는 재귀를 통해 더 간결하게 해결 가능
대표적인 연습 문제
- 두 연결 리스트 병합하기: 두 정렬된 연결 리스트를 병합하여 하나의 정렬된 리스트 만들기
- 리스트 뒤집기: 연결 리스트의 노드 순서를 뒤집기
- k번째 노드 삭제: 끝에서 k번째 노드 찾아 삭제하기
- 팰린드롬 확인: 연결 리스트가 팰린드롬인지 확인하기
- 사이클 찾기: 연결 리스트 내 사이클 감지 및 시작점 찾기
| |